Gallbladder Stone Can Be Removed Without Surgery ?
Gallbladder stone can be removed without surgery ?
Introduction
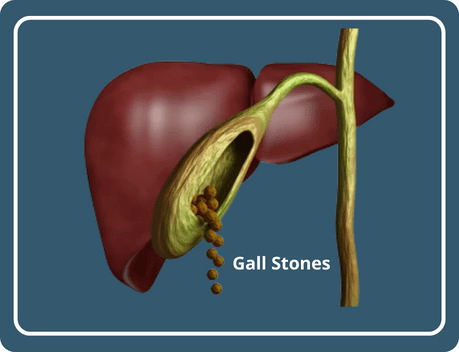 Gallbladder stones, also known as gallstones, can be an extremely painful and concerning health condition. These hardened deposits of digestive fluid within the gallbladder can cause severe discomfort, leading many individuals to consider surgical removal as their only option. However, the good news is that there are alternative treatments available that can help eliminate gallbladder stones without the need for surgery. here we'll explore various non-surgical methods for treating gallbladder stones, providing you with valuable insights and hope for a surgery-free recovery.
Gallbladder stones, also known as gallstones, can be an extremely painful and concerning health condition. These hardened deposits of digestive fluid within the gallbladder can cause severe discomfort, leading many individuals to consider surgical removal as their only option. However, the good news is that there are alternative treatments available that can help eliminate gallbladder stones without the need for surgery. here we'll explore various non-surgical methods for treating gallbladder stones, providing you with valuable insights and hope for a surgery-free recovery.
Understanding Gallbladder Stones
Before delving into the non-surgical treatment options, let's first understand what gallbladder stones are and what causes them. Gallbladder stones, or gallstones, are solid particles that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located just beneath the liver. These stones can vary in size, ranging from tiny grains to larger, more problematic stones. Gallstones are primarily composed of cholesterol, bilirubin, and calcium salts. They form when there is an imbalance in the substances that make up bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder.Risk Factors for Gallbladder Stones
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing gallbladder stones. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures and make informed decisions about their treatment options. Common risk factors include:
-
Age and Gender: Gallstones are more common in individuals over the age of 40 and in women, especially those who are pregnant or taking hormone replacement therapy.
-
Obesity: Excess body weight increases the risk of gallstone formation.
-
Diet: A high-fat, low-fiber diet can contribute to the development of gallstones.
-
Rapid Weight Loss: Losing weight too quickly can lead to the formation of gallstones.
-
Family History: A family history of gallstones can increase your risk of having gallstones.
-
Medical Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, liver disease, and Crohn's disease can increase the risk of gallstones.
Now that we understand gallstones and their risk factors, let's Understand non-surgical treatment options that can help individuals eliminate these painful stones and avoid surgery.
Non-Surgical Gallbladder Stones Treatment Options

1. Lifestyle Modifications
The first step in treating gallbladder stones without surgery involves making significant lifestyle changes. These changes aim to prevent the growth of existing stones and reduce the risk of developing new ones.- Diet Modification: Adopting a low-fat, high-fiber diet can help reduce the burden on your gallbladder. Reducing the intake of saturated fats, cholesterol, and refined sugars can contribute to better gallbladder health.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise not only helps with weight management but also improves overall digestion, reducing the risk of gallstone formation.
- Gradual Weight Loss: If you're overweight, aim for gradual and steady weight loss to minimize the risk of gallstone development associated with rapid weight loss.
2. Medications
Medications can be prescribed by your healthcare provider to help dissolve gallstones or manage gallbladder-related symptoms. These medications are typically considered for individuals who are not suitable candidates for surgery or those who wish to explore non-surgical options.- Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA): UDCA is a medication that can be used to dissolve small cholesterol-based gallstones over time. It may take months to achieve results, and the success rate varies depending on the size and composition of the stones.
- Pain Management: Medications like pain relievers and antispasmodics can help alleviate the discomfort associated with gallstones.
3. Oral Dissolution Therapy
Oral dissolution therapy involves taking medications that help dissolve gallstones gradually. These medications, such as MTBE (methyl tertiary-butyl ether), are ingested orally and work by breaking down the stones over time. This treatment option is most effective for smaller cholesterol-based gallstones.4. Percutaneous Cholecystostomy
In some cases, when a patient is not a suitable candidate for other non-surgical options, a percutaneous cholecystostomy may be performed. This procedure involves the placement of a tube through the skin and into the gallbladder to drain its contents and relieve symptoms. It is often considered a temporary measure until more definitive treatment can be pursued.Other Therapies
Certain alternative therapies, such as herbal remedies and gallbladder flushes, are sometimes explored by individuals seeking non-surgical treatment. it's crucial to approach these with caution and consult with a healthcare professional, as their safety and effectiveness are not well-established.