Hernia Treatment in Ahmedabad: Surgical & Non-Surgical Solutions Explained
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the muscle or connective tissue that holds it in place. This condition is often visible as a bulge or lump and can cause significant discomfort. If you're looking for Hernia Treatment in Ahmedabad, it's important to understand the different types of hernias, symptoms, and the most effective treatment options available. This guide explains both surgical and non-surgical solutions to help you make an informed decision.
What is a Hernia?
A hernia occurs when an organ or fat pushes through a weak or damaged area in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. Hernias can appear in various parts of the body, most commonly in the abdomen, groin, and upper thigh. While some hernias are not painful, they can become uncomfortable and lead to serious complications if left untreated.
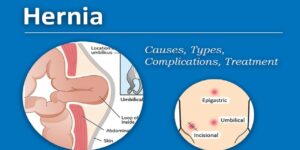
Types of Hernias
-
Inguinal Hernia: The most common type, occurring in the groin area.
-
Umbilical Hernia: A bulge near the belly button, often seen in infants but can also occur in adults.
-
Hiatal Hernia: When part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity.
-
Incisional Hernia: Develops at the site of a previous surgical incision.
-
Femoral Hernia: A less common type that occurs in the upper thigh near the groin.
Symptoms of a Hernia
While some hernias may not cause immediate symptoms, most individuals will experience some of the following signs:
-
Visible bulge in the affected area, often more prominent when coughing or standing.
-
Pain or discomfort at the site, especially when lifting, bending, or after physical activity.
-
Feeling of heaviness or pressure in the abdomen.
-
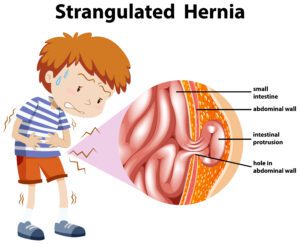
Nausea, vomiting, or constipation (in severe cases, especially if the hernia is strangulated).
If you notice any of these symptoms, it's important to consult a healthcare provider promptly. Untreated hernias can lead to complications, including bowel obstruction or strangulation, which require emergency treatment.
Non-Surgical Hernia Treatment Options
In some cases, hernias may not require immediate surgery, especially if the hernia is small and not causing any significant symptoms. Here are the non-surgical hernia treatment options:
1. Watchful Waiting
If your hernia is small and not causing any discomfort, your doctor may recommend a wait-and-see approach, especially if you are not experiencing any significant symptoms. Regular check-ups will help monitor the size of the hernia and ensure that it doesn't become more problematic.
2. Hernia Belts and Trusses
Hernia belts or trusses are supportive garments designed to hold the hernia in place and reduce the bulging. These are often recommended for individuals who are not candidates for surgery or those with a very mild hernia. While these devices may reduce discomfort, they do not treat the hernia and are typically used as a temporary solution.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle changes can help manage hernia symptoms and prevent them from getting worse. These include:
-
Avoiding heavy lifting: Straining can make the hernia worse.
-
Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can put added pressure on the abdomen, worsening the hernia.
-
Eating a high-fiber diet: This helps avoid constipation and straining during bowel movements, which can aggravate hernias.
-
Gentle exercises: Low-impact exercises can help strengthen muscles around the hernia site without causing additional strain.
While these methods can help manage symptoms, they don’t cure the hernia, and surgery may still be necessary in the future.
Surgical Solutions for Hernia Treatment
When a hernia causes significant pain, grows in size, or leads to complications, surgery is typically the most effective solution. Here are the most common surgical treatments for hernias:
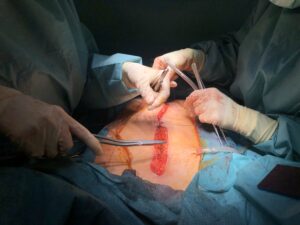
1. Laparoscopic Surgery (Minimally Invasive)
Laparoscopic surgery is a modern, minimally invasive method for hernia repair. A small incision is made in the abdomen, and a tiny camera is inserted to view the hernia site. The surgeon then uses small instruments to repair the hernia with mesh material.
Benefits of laparoscopic surgery:
-
Smaller incisions result in less pain and quicker recovery.
-
Shorter hospital stay and faster return to normal activities.
-
Less scarring compared to traditional open surgery.
Laparoscopic surgery is ideal for most types of hernias and has become the standard of care due to its numerous advantages over traditional methods.
2. Open Surgery
In open surgery, a larger incision is made in the affected area, and the hernia is pushed back into place. The surgeon then closes the defect in the muscle wall and reinforces it with mesh to prevent recurrence. This technique is commonly used for larger hernias or in cases where laparoscopic surgery may not be suitable.
Advantages of open surgery:
-
Suitable for larger or more complicated hernias.
-
Proven track record with successful outcomes.
However, it involves a longer recovery time and a higher risk of complications such as infection or bleeding compared to laparoscopic surgery.
3. Robotic Surgery
In some advanced medical centres, robotic-assisted surgery is used for hernia repair. This procedure combines the precision of robotic arms with the expertise of a surgeon, allowing for more precise movements and smaller incisions.
Benefits of robotic surgery:
-
Enhanced precision and control, leading to less trauma to the surrounding tissues.
-
Shorter recovery time and less pain post-surgery.
-
Smaller incisions, reducing the risk of infection and scarring.
While robotic surgery is a promising option, it is typically more expensive than traditional laparoscopic surgery and may not be available at all healthcare facilities.
Recovery After Hernia Surgery
After hernia surgery, recovery time can vary based on the type of procedure performed, your general health, and the size of the hernia. Here are some general recovery guidelines:
-
Post-operative care: You will be monitored for a short time after surgery to ensure no complications.
-
Pain management: Pain is usually mild to moderate after laparoscopic surgery and can be controlled with over-the-counter pain medications.
-
Return to work: Most people can return to light work after 1–2 weeks, but it may take 4–6 weeks to return to full activity, especially if the surgery was more extensive.
-
Avoid heavy lifting: Refrain from lifting heavy objects or engaging in strenuous activities for about 6 weeks to avoid straining the repair site.
Follow-up appointments will be scheduled to ensure proper healing and check for any signs of recurrence.
Why Choose Ahmedabad for Hernia Treatment?
Ahmedabad is a healthcare hub with some of the most experienced surgeons and modern medical facilities offering Hernia Treatment in Ahmedabad. Here’s why you should consider Ahmedabad for your hernia treatment:
-
Expert surgeons: Ahmedabad boasts highly skilled surgeons specializing in both laparoscopic and open hernia surgeries.
-
State-of-the-art hospitals: The city is home to advanced medical centres with cutting-edge diagnostic and surgical technology.
-
Comprehensive care: From diagnosis to post-surgery rehabilitation, you’ll receive complete care under one roof.
By choosing a trusted clinic in Ahmedabad, you can ensure you’re receiving world-class care.
When to Seek Emergency Care
If you experience any of the following symptoms, seek emergency medical attention immediately:
-
Sudden severe pain in the abdomen, often indicating strangulation.
-
Nausea, vomiting, or fever, which can signal a bowel obstruction.
-
Inability to pass gas or have a bowel movement, which may indicate a serious complication.
These symptoms require urgent surgical intervention to avoid life-threatening complications.
The Bottom Line
Whether you're dealing with a small bulge or significant pain, Hernia Treatment in Ahmedabad offers a range of surgical and non-surgical options. Minimally invasive procedures like laparoscopic surgery provide excellent results with faster recovery, while open surgery may be required for larger or more complex hernias.
For expert diagnosis and treatment, consult a leading gastroenterologist or surgeon today through drgastro.in to explore the best options for your hernia treatment.