Appendicitis: Signs & Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
Appendicitis occurs when your appendix gets clogged, infected, and inflamed. Your appendix is a small, tube-shaped organ attached to your large intestine. Nobody knows its purpose, but we know that appendicitis is serious. The standard treatment is surgery to remove your appendix.

Overview
What is Appendicitis?
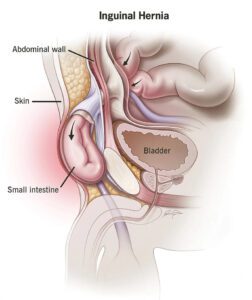
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, a small, finger-like tube located where the large and small intestines meet. This condition is considered a medical emergency and typically requires prompt surgery to remove the appendix. If left untreated, an inflamed appendix can burst, or perforate, spilling infectious materials into the abdominal cavity, which can lead to serious complications.
The exact cause of appendicitis isn't always clear, but it is often the result of a blockage inside the appendix. This blockage can be due to a build-up of hardened stool, foreign bodies, or even cancer. The blockage leads to an infection, as bacteria multiply rapidly in the trapped area. This infection causes the inflammation and swelling associated with appendicitis.
What is acute appendicitis vs. chronic appendicitis?
Acute appendicitis is a condition where the appendix, a small tube-like structure attached to the large intestine, becomes inflamed rapidly. It is typically caused by a blockage inside the appendix.
Chronic appendicitis, on the other hand, refers to a slower, long-term inflammation of the appendix. It is a rarer condition and its exact cause is not as clearly defined as that of acute appendicitis.
How common is appendicitis?
Appendicitis is a relatively common condition. In the United States, it is one of the most frequent causes of acute abdominal pain leading to surgery. Each year, appendicitis affects about 1 in 1,000 people in the U.S. Globally, the incidence rates can vary, but it remains a common surgical emergency worldwide.
The condition most commonly occurs in people between the ages of 10 and 30, but it can happen at any age. The lifetime risk of developing appendicitis is about 8.6% for males and 6.7% for females. This data underscores the fact that appendicitis is a significant health concern, particularly in the younger population.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of appendicitis?
The most common symptoms of appendicitis are abdominal pain, nausea and loss of appetite. There’s a typical way these symptoms may present that can make it easier to recognize appendicitis. But unfortunately, only about half of people with appendicitis have the classic presentation of symptoms. Kids, elderly adults and pregnant people may be less likely to present with typical symptoms.
What are the early signs of appendicitis?
Early signs of appendicitis typically include a dull pain around the navel or upper abdomen, which gradually sharpens and moves to the lower right side. This pain often worsens with movement, coughing, or deep breathing. This is often accompanied by loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting. A low-grade fever and a general feeling of malaise may also be present. These symptoms can mimic other conditions, so it's important to seek prompt medical attention if they persist or worsen.
What are other possible symptoms of appendicitis?
Other possible symptoms of appendicitis can vary depending on the individual and the stage of the condition. These may include:
Diarrhea or Constipation: Some individuals may experience changes in bowel habits, including diarrhea or constipation.
Urinary Symptoms: Difficulties in urination, such as pain or an urge to urinate more frequently, can occur if the appendix is near the bladder or urinary tract.
Rebound Tenderness: Pain that is worse upon releasing pressure on the abdomen, a sign doctors often look for during a physical exam.
Low Back Pain or Pain in the Rectum or Pelvis: Less common, but can occur depending on the position of the appendix.
Anorexia: A lack of appetite is a common symptom.
Mild Fever that May Progress: Initially, the fever may be low-grade but can increase as the condition worsens.
How can I check for appendicitis at home?
If you're concerned about appendicitis, it's crucial to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis. However, there are some signs that providers commonly use to assess for appendicitis which you can be aware of:
- McBurney's Sign: This involves checking for tenderness at McBurney's point, typically the most common location of the appendix. It's located by drawing an imaginary line from the ASIS (the bony protrusion near your hip) to your belly button. The point of interest is approximately two inches from the ASIS, or one-third of the way along this line.
- Blumberg's Sign: Also known as rebound tenderness, this sign is positive if you feel increased pain upon releasing pressure from the sore area.
- Dunphy's Sign: A worsening of pain when coughing can be indicative of appendicitis.
- Rovsing's Sign: This occurs when pressure applied to the lower left side of your abdomen causes pain on the lower right side.
- Psoas Sign: If your appendix is located behind your colon, it may irritate your psoas muscle. You might instinctively flex your right hip to alleviate this pain. Healthcare providers may check for pain during extension or outward rotation of your right hip, indicating a positive psoas sign. If rotating it inward causes pain, it's known as the obturator sign.
What other conditions might be confused with appendicitis?
Appendicitis can sometimes be confused with other conditions because its symptoms are similar to those of several other illnesses. Some common conditions that might be mistaken for appendicitis include:
- Gastroenteritis
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
- Gallbladder Problems
- Intestinal Obstruction
- Meckel's Diverticulitis
- Ovarian Cyst Rupture or Torsion
- Kidney Stones
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Ectopic Pregnancy
What causes appendicitis?
Appendicitis, the inflammation of the appendix, can be caused by several factors, primarily involving an obstruction of the appendix. The most common causes include:
- Blockage by Fecal Matter: Accumulation of fecal material can block the opening of the appendix into the cecum, the first part of the large intestine.
- Enlarged Lymphoid Follicles: These structures in the appendix can enlarge due to infections, such as a gastrointestinal viral infection, leading to blockage.
- Intestinal Worms: Parasitic infections can cause obstruction of the appendix.
- Trauma: A direct injury to the abdomen can sometimes result in appendicitis if it leads to inflammation and swelling of the appendix.
- Tumors: Both benign and malignant tumors can obstruct the appendix and cause appendicitis.
- Foreign Bodies: Rarely, ingestion of foreign objects can lead to blockage and inflammation of the appendix.
What causes chronic appendicitis?
Chronic appendicitis involves ongoing inflammation of the appendix, typically resulting from a partial obstruction by fecal matter, calcified deposits (appendicoliths), or swollen lymphoid tissue. This differs from acute appendicitis as the symptoms are milder and more persistent. Repeated minor infections in the appendix can also cause chronic inflammation, leading to a prolonged period of discomfort rather than intense, rapid-onset symptoms
Is appendicitis genetic?
Appendicitis is not typically considered a genetic condition. It is usually caused by environmental factors, like blockages in the appendix, rather than hereditary factors. While some genetic predispositions may influence one's susceptibility to inflammation or infection, leading to appendicitis, these are not the primary causes. A Family history of appendicitis generally does not significantly increase an individual's risk.
Can stress cause appendicitis?
Stress does not directly cause appendicitis, which is usually due to an obstruction leading to infection in the appendix. However, chronic stress can affect the body in ways that might indirectly increase the risk of developing appendicitis, such as by altering immune function and gut health. Nonetheless, this connection is not clearly established in medical research and is considered a secondary factor if at all relevant.
Can food cause appendicitis?
Specific foods do not directly cause appendicitis. Appendicitis is usually caused by a blockage in the appendix, often due to fecal matter, not by eating particular types of food. There have been rare reports of an undigested seed or nut getting stuck in the opening to the appendix and causing inflammation.
What are the possible complications of appendicitis?
Appendicitis, an inflammation of the appendix, can lead to several complications if not treated promptly. The possible complications include:
Appendix Rupture: If appendicitis is not treated, the appendix can burst, releasing bacteria and other harmful substances into the abdominal cavity. This can lead to a serious condition called peritonitis, an inflammation of the tissue lining the abdominal wall.
Abscess Formation: After the appendix ruptures, an abscess may form around the infected area. This is a pocket of infection that can cause further complications.
Peritonitis: As mentioned, peritonitis is the infection and inflammation of the peritoneum (the lining of the abdominal cavity). This condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical treatment.
Sepsis: If the infection spreads beyond the appendix, it can lead to sepsis, a dangerous and potentially life-threatening condition caused by the body's response to infection.
Intestinal Obstruction: In some cases, inflammation resulting from appendicitis can cause the intestines to become blocked.
Chronic Pain: Rarely, individuals can experience long-term pain in the abdomen after appendicitis, particularly if it was complicated or not adequately treated.
Have any Doubts or Concerns about Appendicitis?
Consult Us