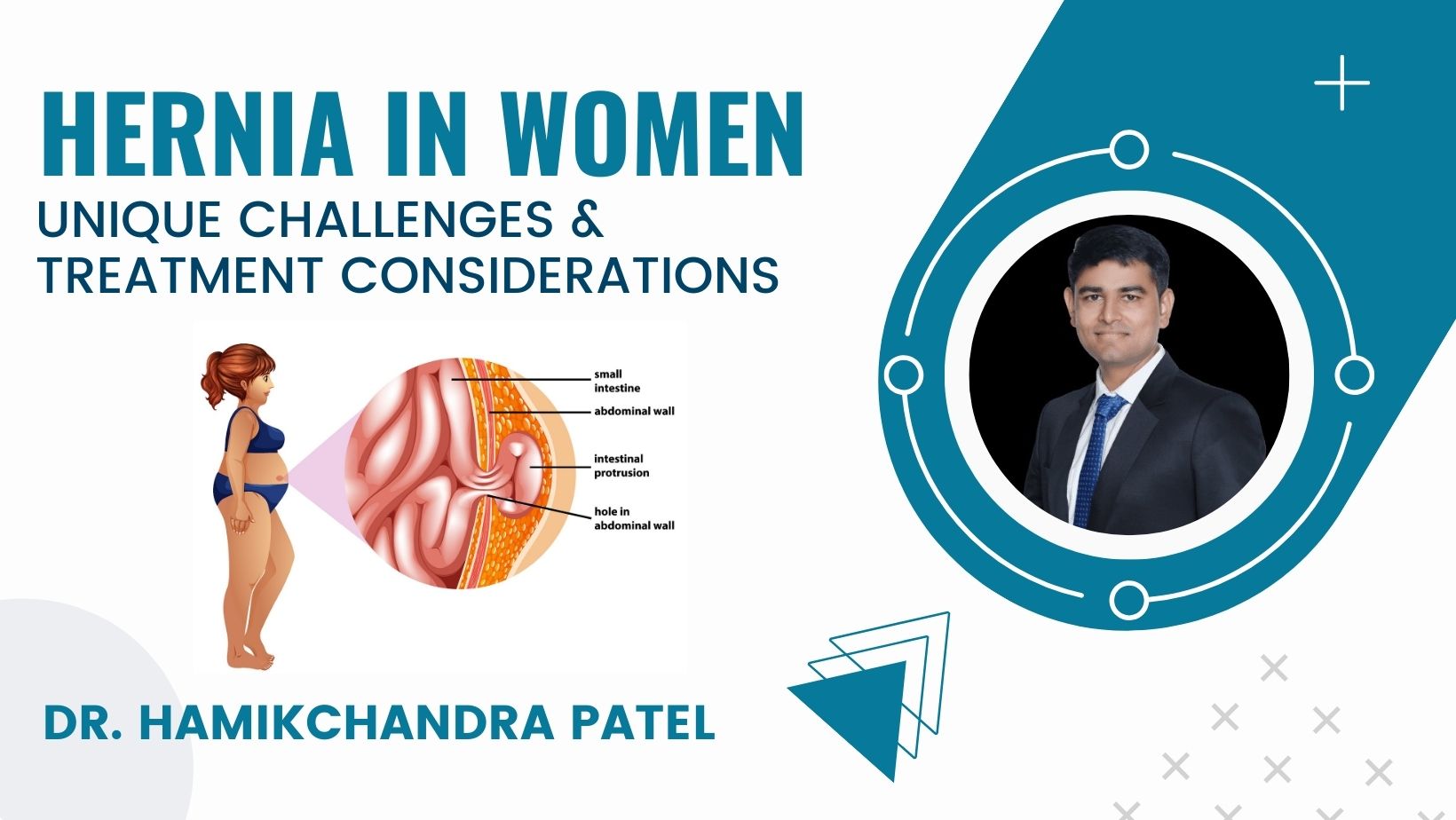
Hernia in Women: Unique Challenges and Treatment Consideration : Dr. Hamikchandra Patel

Introduction: Hernia in Women
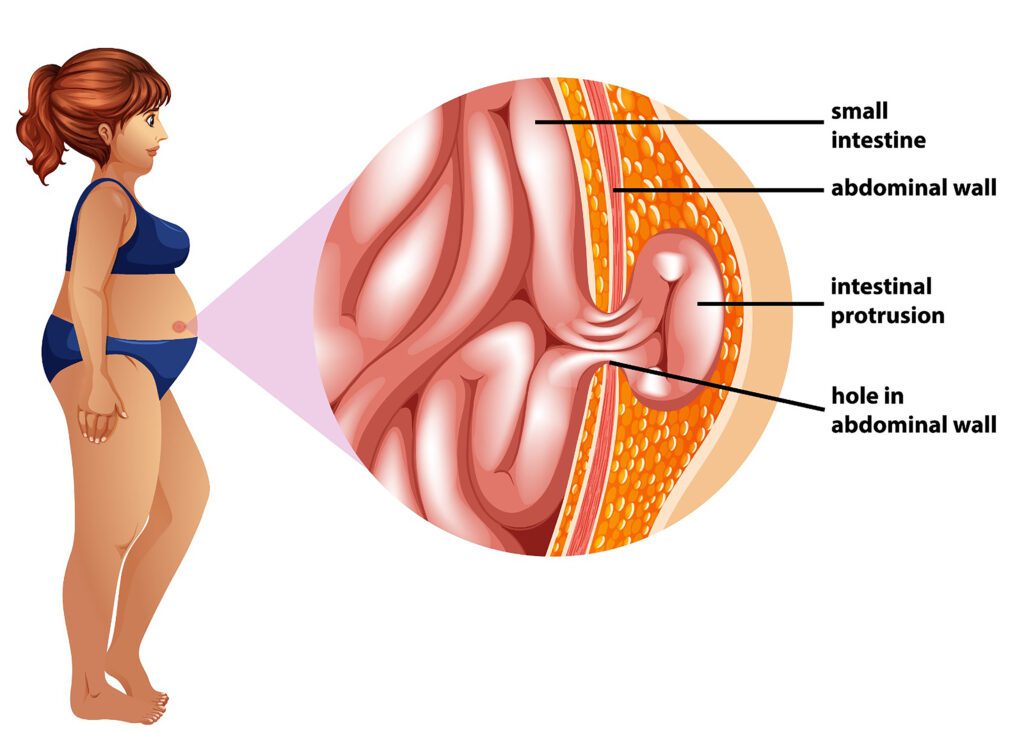
Hernia in women, A hernia occurs when an internal organ or other body part protrudes through the wall of muscle or tissue that normally contains it. In women, hernias can occur in various locations, but the most common types are:
Inguinal Hernias: Although more common in men, inguinal hernias can occur in women. This type of hernia happens when tissue, such as part of the intestine, protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles, often appearing in the groin area.
Femoral Hernias: More common in women than men, femoral hernias are also situated in the groin area. They occur just below the inguinal ligament, where the femoral artery and vein pass through the muscle wall to enter the thigh.
Incisional Hernias: These can develop after abdominal surgery, where the intestine pushes through the incision scar or surrounding weakened tissue.
Hiatal Hernias: This type occurs when part of the stomach pushes up into the chest cavity through an opening in the diaphragm. While hiatal hernias can affect both genders, certain types may be more prevalent in women.
Umbilical Hernias: Common in newborns, these can also occur in women, particularly during or after pregnancy. This type of hernia is seen around the belly button area.
Hormonal Factors and Hernia Risk in Women

Hernias, can pose a risk to women, and emerging research suggests that hormonal factors play a crucial role in this dynamic.
- Estrogen- a key female hormone
- Influences connective tissue strength and elasticity.
- Fluctuations in estrogen levels, during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, may impact the integrity of abdominal muscles, potentially increasing susceptibility to hernias.
During pregnancy, for instance, elevated estrogen levels can weaken the abdominal wall, making herniation more likely. Further, hormonal changes associated with menopause can lead to a decline in collagen production, affecting tissue strength. Understanding these hormonal intricacies is pivotal for preventive healthcare in women.
Promoting hormonal balance through lifestyle measures, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, may mitigate hernia risks. By comprehensively addressing hormonal factors, we can empower women to proactively manage their health and reduce the incidence of hernias.
Tailoring Treatment For Female Hernia Patients
Treatment for female hernia patients is essential for optimal healthcare outcomes. hernias are commonly associated with men, women also experience this condition, and their unique anatomical and physiological factors necessitate a customized approach. Understanding the intricacies of female hernias, such as femoral hernia and
inguinal hernia, is paramount for accurate diagnosis and effective intervention.

Tailored diagnostic strategies, including imaging techniques suitable for female anatomy, are crucial. Surgeons must consider factors like pregnancy history and hormonal influences when crafting treatment plans. Personalized postoperative care should address the specific needs and concerns of female patients, promoting a faster and smoother recovery.
By acknowledging the nuances of hernias in women and tailoring treatment accordingly, healthcare providers can enhance patient outcomes and quality of life. A holistic approach, combining medical expertise and gender-sensitive care, ensures that female hernia patients receive the attention and interventions necessary for their unique health journey.
Pregnancy and Hernia: What Mothers Need to Know
Pregnancy is a transformative journey, but for some mothers, it may intersect with the challenge of hernias. Hernias occur when organs protrude through weakened muscles, and the strain of pregnancy can exacerbate this condition. While not all pregnant women with hernias experience complications, awareness is crucial.

Firstly, consult with a healthcare professional to assess the hernia's severity and potential risks. Mild cases may require monitoring, while severe instances might necessitate surgical intervention post-pregnancy.
Discuss symptoms, concerns, and any changes promptly to ensure a comprehensive care plan. By staying informed and proactive, women can optimize both their maternal and hernia-related health, fostering a safe and fulfilling pregnancy journey.
Treatment of Hernia in Women
The treatment of hernia in women typically involves surgical intervention, especially if the hernia is causing pain or other symptoms. The most common procedure is laparoscopic surgery, a minimally invasive technique that uses small incisions and a camera. Recovery time is usually short, and the risk of recurrence is low. This approach allows for quicker healing and less post-operative discomfort compared to traditional open surgery. Regular follow-ups and lifestyle adjustments, such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding heavy lifting, are crucial for a successful outcome
Advantages of Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
1. Reduced Pain and Scarring
2. Faster Recovery Time
3. Lower Risk of Infection
The treatment of hernia in women typically involves surgical intervention, especially if the hernia is causing pain or other symptoms. The most common procedure is laparoscopic surgery, a minimally invasive technique that uses small incisions and a camera. Recovery time is usually short, and the risk of recurrence is low. This approach allows for quicker healing and less post-operative discomfort compared to traditional open surgery. Regular follow-ups and lifestyle adjustments, such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding heavy lifting, are crucial for a successful outcome
This comprehensive blog aims to bridge the information gap surrounding hernias in women, offering insights into their causes, unique challenges, and personalized treatment approaches
If you or someone you know is dealing with an issue, remember that early diagnosis and timely treatment are essential for a successful recovery. If you have any concerns or questions about Treatment of Hernia in Women, don't hesitate to consult a
Dr. Hamikchandra Patel. He is one the Best Surgical Gastroenterologist in Ahmedabad. For more Information you can Visit
Dr. Gastro.
Have any Doubts or Concerns about Hernia in Women?
Consult Us
 While hernias typically do not heal on their own, there are non-surgical approaches to manage them. These approaches may be suitable for certain individuals, especially those with small hernias or underlying health concerns that make surgery a less desirable option. Non-surgical management may include:
While hernias typically do not heal on their own, there are non-surgical approaches to manage them. These approaches may be suitable for certain individuals, especially those with small hernias or underlying health concerns that make surgery a less desirable option. Non-surgical management may include:
 The recovery period following hernia surgery varies depending on the type of procedure, the patient's overall health, and the size of the hernia. In general, most patients can expect the following during their recovery:
The recovery period following hernia surgery varies depending on the type of procedure, the patient's overall health, and the size of the hernia. In general, most patients can expect the following during their recovery:


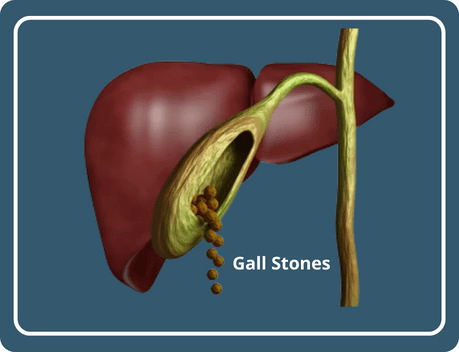 Gallbladder stones, also known as gallstones, can be an extremely painful and concerning health condition. These hardened deposits of digestive fluid within the gallbladder can cause severe discomfort, leading many individuals to consider surgical removal as their only option. However, the good news is that there are alternative treatments available that can help eliminate gallbladder stones without the need for surgery. here we'll explore various non-surgical methods for treating gallbladder stones, providing you with valuable insights and hope for a surgery-free recovery.
Gallbladder stones, also known as gallstones, can be an extremely painful and concerning health condition. These hardened deposits of digestive fluid within the gallbladder can cause severe discomfort, leading many individuals to consider surgical removal as their only option. However, the good news is that there are alternative treatments available that can help eliminate gallbladder stones without the need for surgery. here we'll explore various non-surgical methods for treating gallbladder stones, providing you with valuable insights and hope for a surgery-free recovery.

 Hernias, can pose a risk to women, and emerging research suggests that hormonal factors play a crucial role in this dynamic.
Hernias, can pose a risk to women, and emerging research suggests that hormonal factors play a crucial role in this dynamic.
 Tailored diagnostic strategies, including imaging techniques suitable for female anatomy, are crucial. Surgeons must consider factors like pregnancy history and hormonal influences when crafting treatment plans. Personalized postoperative care should address the specific needs and concerns of female patients, promoting a faster and smoother recovery.
By acknowledging the nuances of hernias in women and tailoring treatment accordingly, healthcare providers can enhance patient outcomes and quality of life. A holistic approach, combining medical expertise and gender-sensitive care, ensures that female hernia patients receive the attention and interventions necessary for their unique health journey.
Tailored diagnostic strategies, including imaging techniques suitable for female anatomy, are crucial. Surgeons must consider factors like pregnancy history and hormonal influences when crafting treatment plans. Personalized postoperative care should address the specific needs and concerns of female patients, promoting a faster and smoother recovery.
By acknowledging the nuances of hernias in women and tailoring treatment accordingly, healthcare providers can enhance patient outcomes and quality of life. A holistic approach, combining medical expertise and gender-sensitive care, ensures that female hernia patients receive the attention and interventions necessary for their unique health journey.
 Firstly, consult with a healthcare professional to assess the hernia's severity and potential risks. Mild cases may require monitoring, while severe instances might necessitate surgical intervention post-pregnancy.
Discuss symptoms, concerns, and any changes promptly to ensure a comprehensive care plan. By staying informed and proactive, women can optimize both their maternal and hernia-related health, fostering a safe and fulfilling pregnancy journey.
Firstly, consult with a healthcare professional to assess the hernia's severity and potential risks. Mild cases may require monitoring, while severe instances might necessitate surgical intervention post-pregnancy.
Discuss symptoms, concerns, and any changes promptly to ensure a comprehensive care plan. By staying informed and proactive, women can optimize both their maternal and hernia-related health, fostering a safe and fulfilling pregnancy journey.