Comprehensive Guide to Hernia Treatment: Options, Recovery, and Prevention
Admin2024-04-18T10:50:44+00:00Introduction: Comprehensive Guide to Hernia Treatments
A hernia is a medical condition that occurs when an organ or fatty tissue squeezes through a weak spot in a surrounding muscle or connective tissue called fascia. The most common types of hernias are in the abdomen, though they can also occur in the upper thigh, belly button, and groin areas. Recognizing the signs and understanding the treatments available is essential for those affected and can prevent further complications.Understanding Hernias
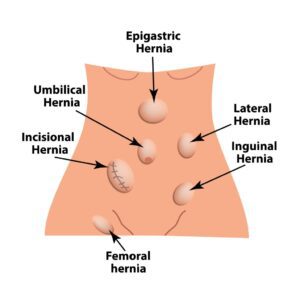
Hernias come in various forms, each with its characteristics:- Inguinal Hernia: The most common type, occurring when the intestines break through a weak spot in the lower abdominal wall,
often in the inguinal canal. This type is more common in men than women.

- Femoral Hernia: Less common and more likely to affect women, these occur when fatty tissue or a part of the intestine protrudes into the groin at the top of the inner thigh.
- Umbilical Hernia: These appear near the belly button and are most common in newborns, though they can also affect adults with increased abdominal pressure.
- Incisional Hernia: Can occur after abdominal surgery, where the intestine pushes through the abdominal wall at the site of previous surgery.
- Hiatal Hernia: This type occurs when part of your stomach protrudes up through the diaphragm into your chest cavity.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
While some hernias are asymptomatic, others may present symptoms such as pain or discomfort, especially when bending over, coughing, or lifting. The most noticeable sign is a bulge or lump in the affected area. Diagnosis involves a physical examination, and sometimes imaging tests, such as an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, to confirm the presence of a hernia.Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Treatments
Not all hernias require immediate surgery. Small, asymptomatic hernias may be managed through watchful waiting. Lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, eating a high-fiber diet, and avoiding heavy lifting, can also help.Surgical Treatments
For hernias causing pain or other symptoms, surgery is often recommended to prevent complications. The two main surgical options are:- Open Hernia Repair: An incision is made near the hernia site, the protruding tissue is pushed back into place, and the weakened area is sewn and sometimes reinforced with a synthetic mesh.
- Laparoscopic (Minimally Invasive) Hernia Repair: Involves smaller incisions and the use of a laparoscope to repair the hernia with mesh. This method typically offers quicker recovery times and less post-operative pain.
Recovery Process
Recovery time varies based on the type of surgery performed and the patient's overall health. Patients can often return to light activities within a few days but may need to avoid strenuous activities for several weeks. Following the surgeon’s post-operative instructions is crucial for a smooth recovery.Preventing Hernias
Some hernias, particularly those that are congenital, may not be preventable. However, you can reduce your risk by:- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Lifting objects carefully and using the legs rather than the back.
- Avoiding smoking, as it can weaken the muscles.
- Managing chronic coughs or constipation, which can contribute to hernia formation.